More Electronic Enclosure Manufacturers
Applications of Electronic Enclosures
Electronic enclosures are crucial for housing and protecting electronic devices across various industries and environments. In industrial settings, metal enclosures protect sensitive electronics from dust, moisture, and harsh conditions, ensuring the reliability of critical machinery and control systems. In consumer electronics, plastic enclosures offer both protection and aesthetic appeal for smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. Medical equipment relies on these enclosures to preserve the integrity of delicate devices and ensure patient safety. In the automotive sector, enclosures shield electronic modules from vibrations, temperature changes, and debris. They are also essential in telecommunications, safeguarding networking equipment from weather and vandalism. Additionally, outdoor applications like solar power systems and remote sensors depend on enclosures to protect electronics from harsh environmental conditions.
History of Electronic Enclosures
Engineers initially designed electronic enclosures to protect individuals from live electrical components exposed through cutouts. Cutouts, consisting of copper bars and an insulated T handle, functioned as switches. Operators would pull the T handle to operate these switches. However, the live parts of the cutouts were exposed, posing a danger to humans. To mitigate this risk, manufacturers began installing cutouts in wooden boxes. This practice was also applied to switchboards used for connecting phone calls from 1878 to the 1960s.
Wooden enclosures served their purpose for a while, but as electricity became common in homes during the 1920s and 1930s, problems emerged. Homeowners found that electrical components within these wooden cabinets could loosen and overheat, causing fires. In response, manufacturers began using flame-retardant metals, such as steel, for cabinets.
Today, electricity has reached levels of sophistication that early inventors like Tesla could scarcely envision. This evolution has led to the development of modern electronic enclosures, now crafted from metals and cutting-edge thermoplastic materials unknown to early engineers. These enclosures are remarkably adaptable, protecting electronic devices of all configurations and sensitivities. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of these enclosures will only increase.
How Electronic Enclosures Work
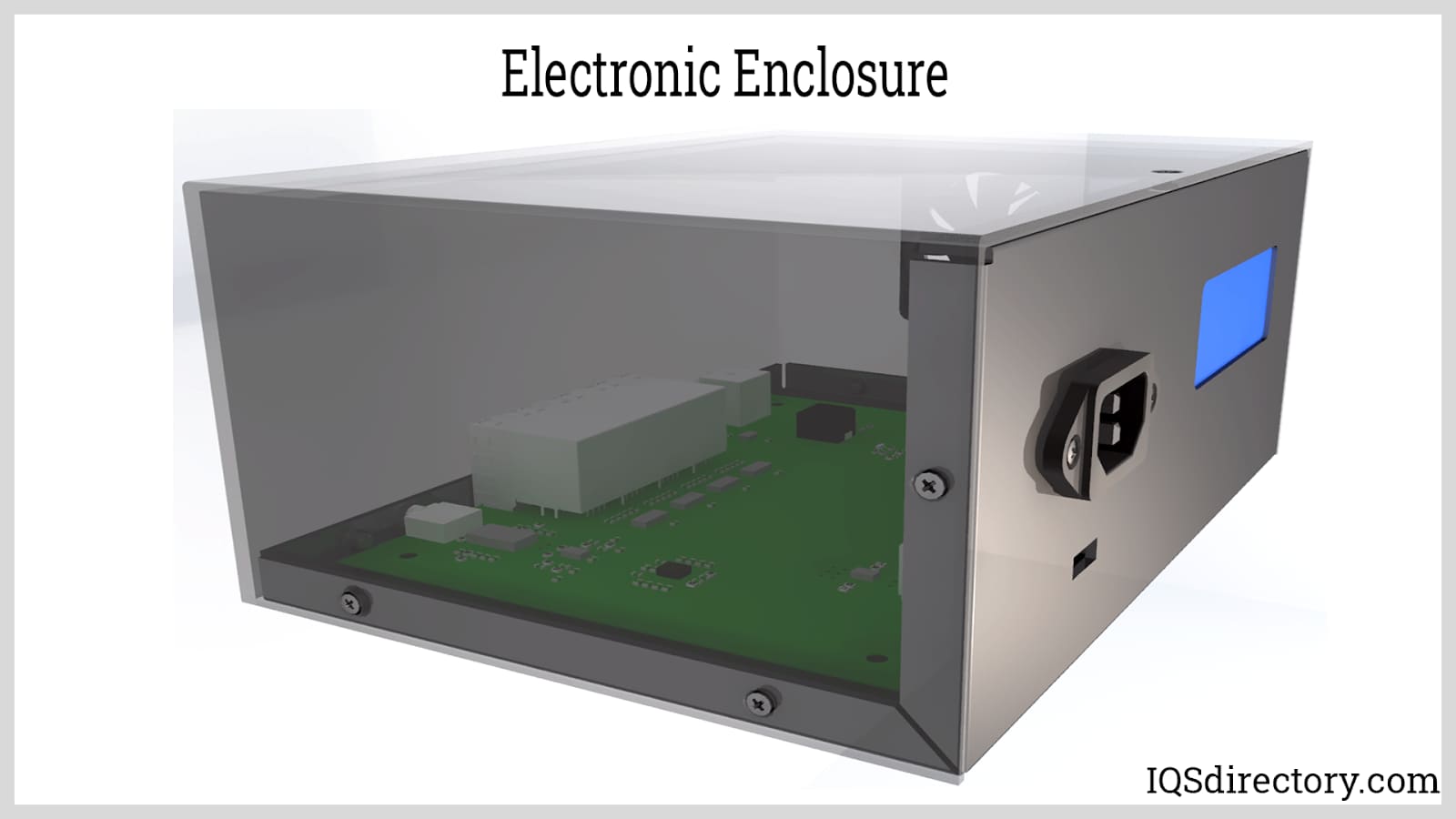
Electronic enclosures are essential for protecting electronic devices and components from external factors, ensuring their functionality and longevity. They provide a secure environment that shields sensitive electronics from various hazards.
The physical structure of the enclosure acts as a barrier against dust, moisture, and contaminants that could cause short circuits or corrosion. Enclosures made from materials like metal, plastic, or composites offer varying levels of protection based on the application’s needs.
Moreover, electronic enclosures often include features like gaskets, seals, or o-rings to create a tight seal, preventing the ingress of water, dust, and foreign particles. These seals are strategically placed at critical access points, such as cable entry points and removable panels, to maintain the enclosure’s integrity.
Managing thermal regulation is essential for electronic enclosures. When electronic components produce heat during operation, the enclosure must effectively manage this heat to prevent overheating and potential damage. To ensure optimal airflow and cooling, we integrate features like vents, fans, or heat sinks into many enclosures.
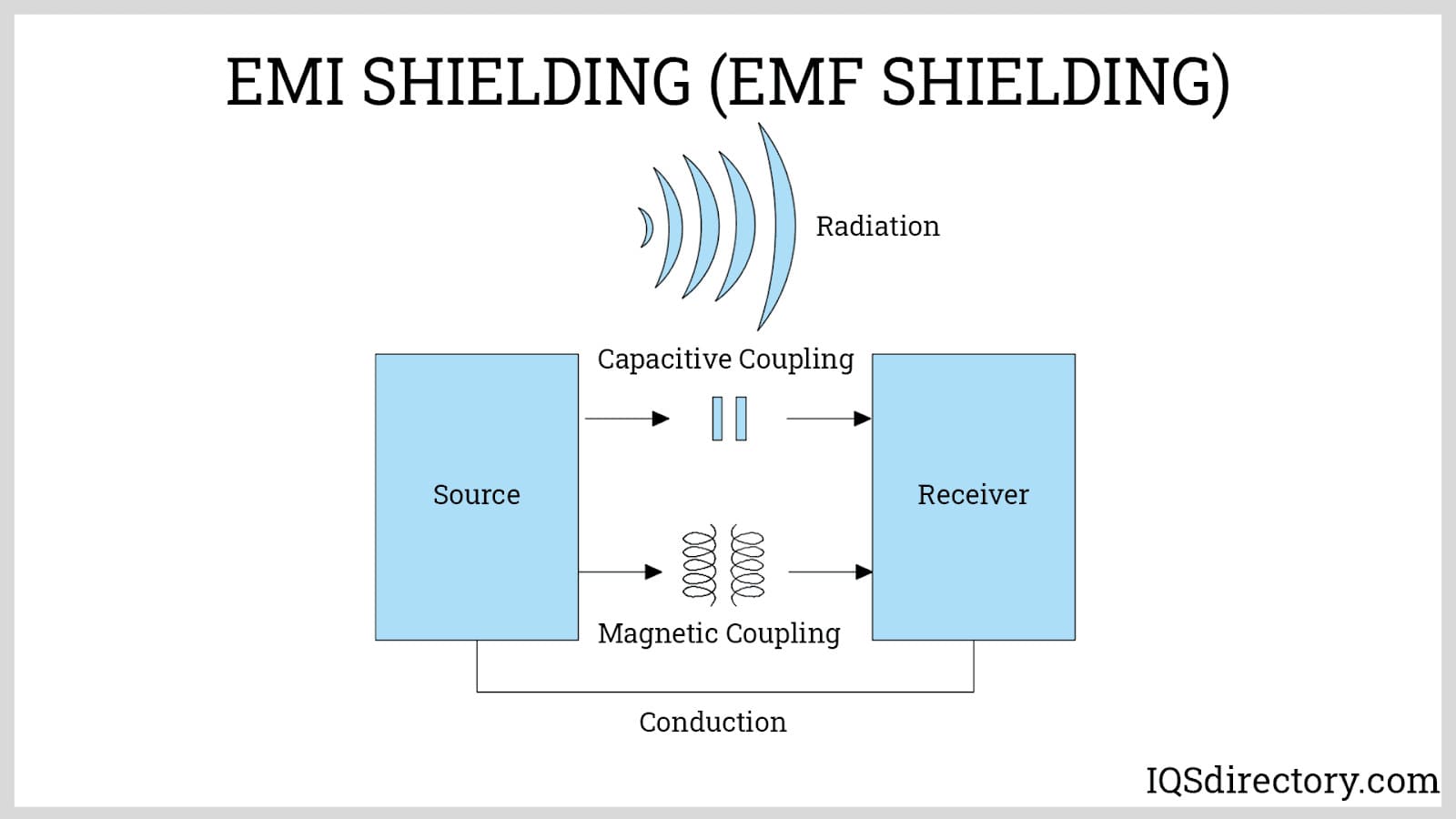
Another critical function of certain electronic enclosures is mitigating electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). By using conductive materials, we design these enclosures to contain electromagnetic emissions and block external interference from affecting the enclosed electronics.
Moreover, electronic enclosures provide physical protection for sensitive electronic components. These enclosures shield the components from impacts and vibrations, preventing malfunction or damage.
Electronic enclosures are often designed to meet industry standards like IP (Ingress Protection) ratings or NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) standards, which specify the level of protection against environmental factors. These enclosures combine physical durability, effective sealing, thermal management, and EMI/RFI shielding to ensure a secure environment for electronic devices and equipment. By safeguarding against environmental and external influences, electronic enclosures are essential for maintaining the performance and longevity of electronic systems in various applications.
Types of Electronic Enclosures
NEMA enclosures, rated by the National Electronics Manufacturers Association (NEMA), must be completely sealed without any partially punched holes or openings, except for those specifically designed for oil and dust-tight mechanisms. Hinged doors on these enclosures require a tool for access and should have an external mounting system. For a dependable and safe electronic enclosure, ensure it has a NEMA certification and discuss your needs with your supplier.
Computer enclosures are crafted to safeguard computer components from dust, debris, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). These enclosures are usually made from steel or aluminum and are coated to block EMI.
Mounted enclosures are designed to be affixed using fasteners or self-tapping screws, with pre-drilled holes in the bottom or back. They are often used to house equipment like wireless connections in warehouse environments.
Rack mount enclosures consist of frames with extending edges or mounting slots, designed for securing electronics. These enclosures frequently house large devices such as computer servers and audio equipment. Typically, they are made from aluminum or steel, with the enclosure itself being a metal structure reinforced with durable plastic. They often feature panels and lockable doors for added security.
Fiberglass enclosures, constructed from fiberglass, offer outstanding electrical insulation and resistance to chemicals, heat, corrosion, and impact. They also support high tensile loads. Because of these attributes, we frequently use fiberglass enclosures in outdoor settings and environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or corrosive materials.
ABS enclosures, crafted from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), offer excellent electrical insulation, shock absorption, impact resistance, and lightweight properties. These features make them ideal for handheld and small pocket devices.
Polycarbonate enclosures perform exceptionally well in cold environments, blocking temperature interference effectively. Their moldability makes them perfect for applications requiring complex or small enclosures.
Stainless steel enclosures are ideal for high-energy applications, such as heat exchangers, due to their ability to absorb and dissipate heat, preventing component overheating. They are also strong and corrosion-resistant.
Aluminum enclosures, known for their strength, durability, and lightweight properties, are produced through extrusion or die-casting. These enclosures excel in conducting electricity and heat, making them suitable for moist indoor environments.
Designing Electronic Enclosures
Manufacturing electronic enclosures involves techniques such as thermoplastic molding, die casting, and extrusion. A diverse range of materials, including fiberglass, stainless steel, aluminum, ABS, and Kevlar, are used to construct these enclosures. When selecting materials, manufacturers evaluate attributes like robustness, thermal insulation, heat transfer, corrosion resistance, vibration absorption, and security. The chosen material must safeguard the electronic components from environmental threats, including extreme temperatures, moisture, explosions, vibrations, weight pressures, and vandalism.
Customizing Electronic Enclosures
Manufacturers prioritize understanding the specific threats your application aims to protect against when considering electronic instrument enclosures. These enclosures typically focus on various protective measures, including impact shielding, heat shielding, static shielding, magnetic shielding, and both dirt and waterproofing. Each of these aspects plays a crucial role in ensuring the durability and reliability of electronic components in diverse environments.
Impact shielding, also known as shock shielding, is essential for safeguarding electronic components against jolts, vibrations, and potential damage from drops or collisions. This protective measure is crucial in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of delicate electronic parts, preventing them from breaking or becoming less effective.
Heat shielding is vital for any electrical components through which electricity flows. As currents move through equipment, they generate heat, which can be detrimental to the functionality and longevity of these components. Additionally, electrical parts vulnerable to external heat sources require this type of protection. Heat shielding maintains the efficiency and integrity of equipment by absorbing, reflecting, or dissipating excess heat, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Static shielding involves multiple layers of protection, including external electrostatic discharge (ESD) shielding, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, radio frequency (RF) shielding, and safeguards against electrical surges and sudden charge fluctuations. This type of shielding is vital for ensuring the reliability and functionality of numerous electronic devices, such as smartphones, cables, microwaves, laboratory apparatus, medical equipment, computers, and broadcasting systems, among others.
Magnetic shielding is designed to protect materials from external magnetic forces. These shields function by channeling the magnetic field into themselves, thereby preventing the field from infiltrating the protected area.
On the other hand, dirt and waterproof shielding provides a more practical form of protection. These shields defend electrical components against environmental hazards such as rain, sleet, snow, dirt, and dust. This type of shielding is essential for preventing damage and ensuring the reliable operation of the components.
Manufacturers must first identify which requirements apply to your project. They evaluate the necessary protection level, mounting security, budget constraints, and desired aesthetics. Additionally, the size and shape of your electronic components are crucial. Enclosures can vary from the size of a fingernail to that of a room. While rectangular box enclosures are typical, manufacturers can also create custom plastic or metal enclosures in unique shapes. These can include features such as locking mechanisms, ventilation fans, custom access points, watertight seals, removable panels, and recessed tops for keypads or labels. To find out what a specific manufacturer can offer, discuss your application needs with them directly.
Benefits of Electronic Enclosures
Electronic enclosures offer substantial benefits that improve the performance, durability, and safety of electronic devices in various sectors. They shield sensitive components from external factors like dust, moisture, and debris, thereby extending their operational lifespan. These enclosures also protect against accidental impacts, vibrations, and rough handling, minimizing the risk of expensive repairs or replacements.
Additionally, electronic enclosures enhance thermal regulation by dispersing heat generated during use. With features such as ventilation slots, heat sinks, or fans, they prevent overheating, maintain ideal temperature levels, and avert performance drops or component failure.
Electronic enclosures play a vital role in protecting electronics from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). They employ conductive materials to trap electromagnetic radiation and prevent external disruptions, thereby preserving optimal functionality and signal quality.
In addition, these enclosures assist businesses in conforming to industry standards and regulations. Enclosures that meet IP ratings or NEMA standards provide robust protection against environmental factors, ensuring compliance with safety and quality guidelines and instilling confidence in customers regarding the product’s dependability.
With electronic enclosures, designers gain the ability to customize and adapt their solutions to specific device requirements. By integrating features such as mounting brackets, cable routing, and access points, manufacturers effectively optimize space and improve user experience. Additionally, these enclosures contribute to a product’s visual appeal and user engagement, which in turn strengthens the brand’s reputation and heightens customer satisfaction. In industrial applications, their sturdy construction ensures resilience in harsh conditions and extends the lifespan of critical equipment and machinery.
Electronic enclosures deliver essential benefits, including protection from external elements, efficient thermal management, EMI/RFI shielding, adherence to standards, design flexibility, and enhanced aesthetics. These advantages are crucial for ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of electronic devices across various industries and applications.
Safety and Compliance Standards
In the United States, the standard for enclosures is defined by NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) types. In contrast, countries adhering to IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards should refer to IEC 60529, which provides ingress protection ratings, commonly known as IP codes.
Nema Types
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association assigns a NEMA type to enclosures, with classifications from Type 1 to Type 13. These classifications determine whether an enclosure is suitable for indoor or outdoor environments, its effectiveness in hazardous conditions, and the level of protection it offers for electronic components and wiring. Understanding these classifications is essential. For example, Type 1 enclosures are designed for general indoor use and to prevent accidental contact with the equipment, so they are not appropriate for outdoor applications.
For both indoor and outdoor environments, Type 4X enclosures offer protection from elements such as corrosion, snow, rain, dust, ice, and sleet. In contrast, Type 12 enclosures are designed for indoor industrial use, providing a barrier against dust, grime, lint, and non-corrosive liquids for sensitive electrical components.
Finding the Right Manufacturer
For the ideal enclosure, select a reliable manufacturer that puts your needs first. Start by examining the manufacturers listed on this page, each with unique advantages. Identify the best fit by reviewing their profiles and websites, and then reach out to three or four based on their services. Document your requirements, questions, and concerns beforehand. After engaging with each manufacturer, compare their offerings, prices, and additional services such as after-sales support to make an informed choice. Good luck!



 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services