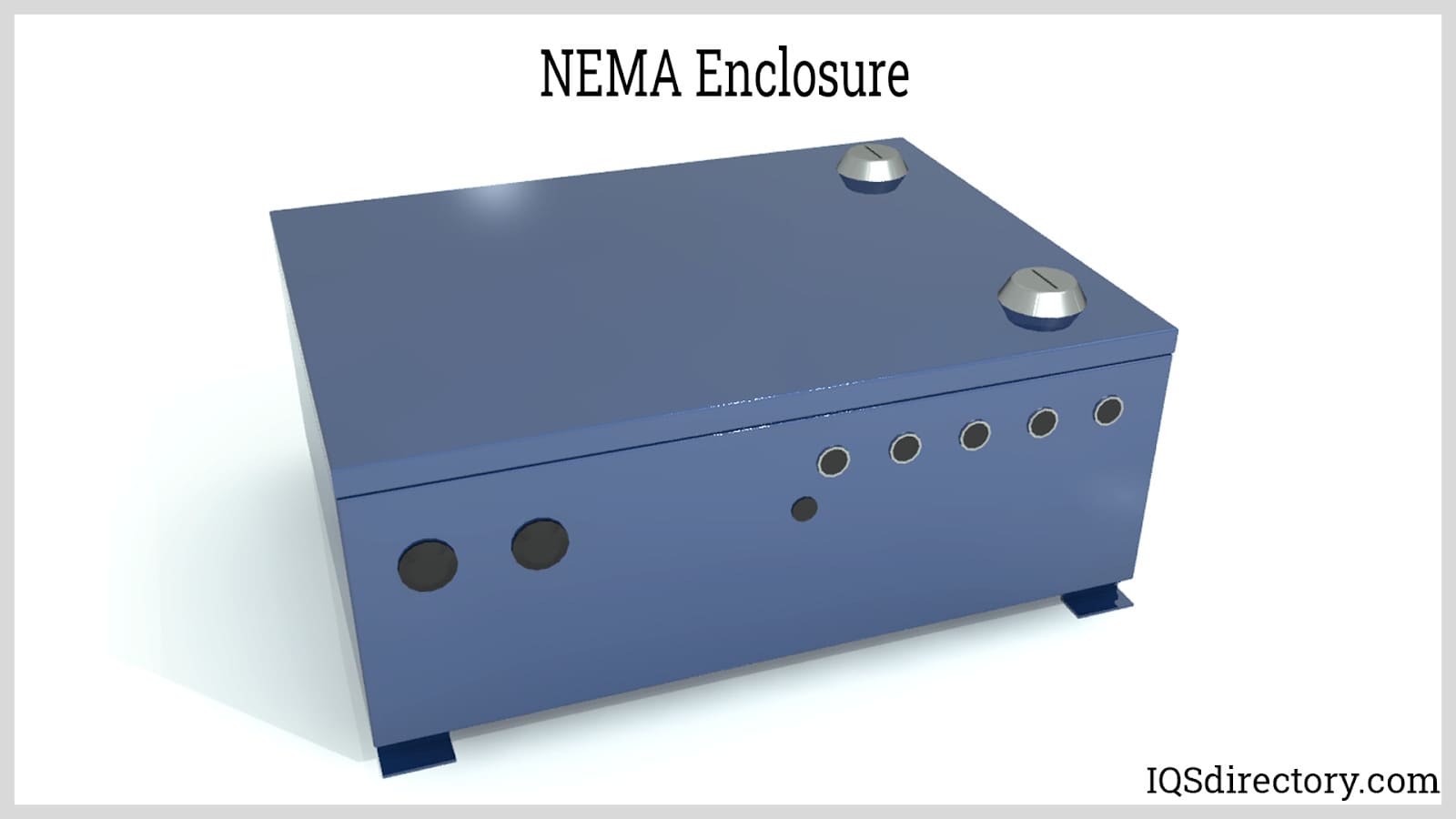
Accidental contact could cause bodily harm and damage the equipment itself. Without a proper shield, electromagnetic interference, or EMI, can disrupt the circuitry of many electronics and interfere with their operation. Read More…
Since 1975, we have been doing precision sheet metal fabrication. Our expertise is in high production, high quality ISO 9000 Certified service. Dedicated manufacturing with on-time delivery. Electronic enclosures, chassis, frames, bracketry to extremely complex weldments and components.
AutomationDirect.com takes pride in being a trusted partner for businesses seeking reliable electronic enclosure solutions. Our team is dedicated to providing exceptional customer service and technical support to ensure that our customers find the perfect products to meet their needs.
EMCOR® Enclosures is a modular enclosure manufacturer and makes related component items as well. Our electronic equipment racks and enclosures feature an extensive selection of rack heights, widths, depths, and styles that target your specific design requirements. A variety of external and internal accessories are available to complete your design. Modified or custom designs are also available....
At Accurate Metal Fabricating, we specialize in crafting precision-engineered electronic enclosures that meet the unique demands of modern industries. With a relentless commitment to quality, we pride ourselves on providing cutting-edge enclosures that safeguard electronic components with unparalleled accuracy. At the heart of our success is a passion for innovation, driving us to create...
Buckeye ShapeForm manufactures electronic enclosures and electrical enclosures that take your company to the next level! Different types include desktop, handheld and rackmount. We will help you with the entire process, from selection, design and customization to finishing.

More Electrical Enclosure Manufacturers
Electrical Enclosures: Types, Applications, Standards, and Selection Guide
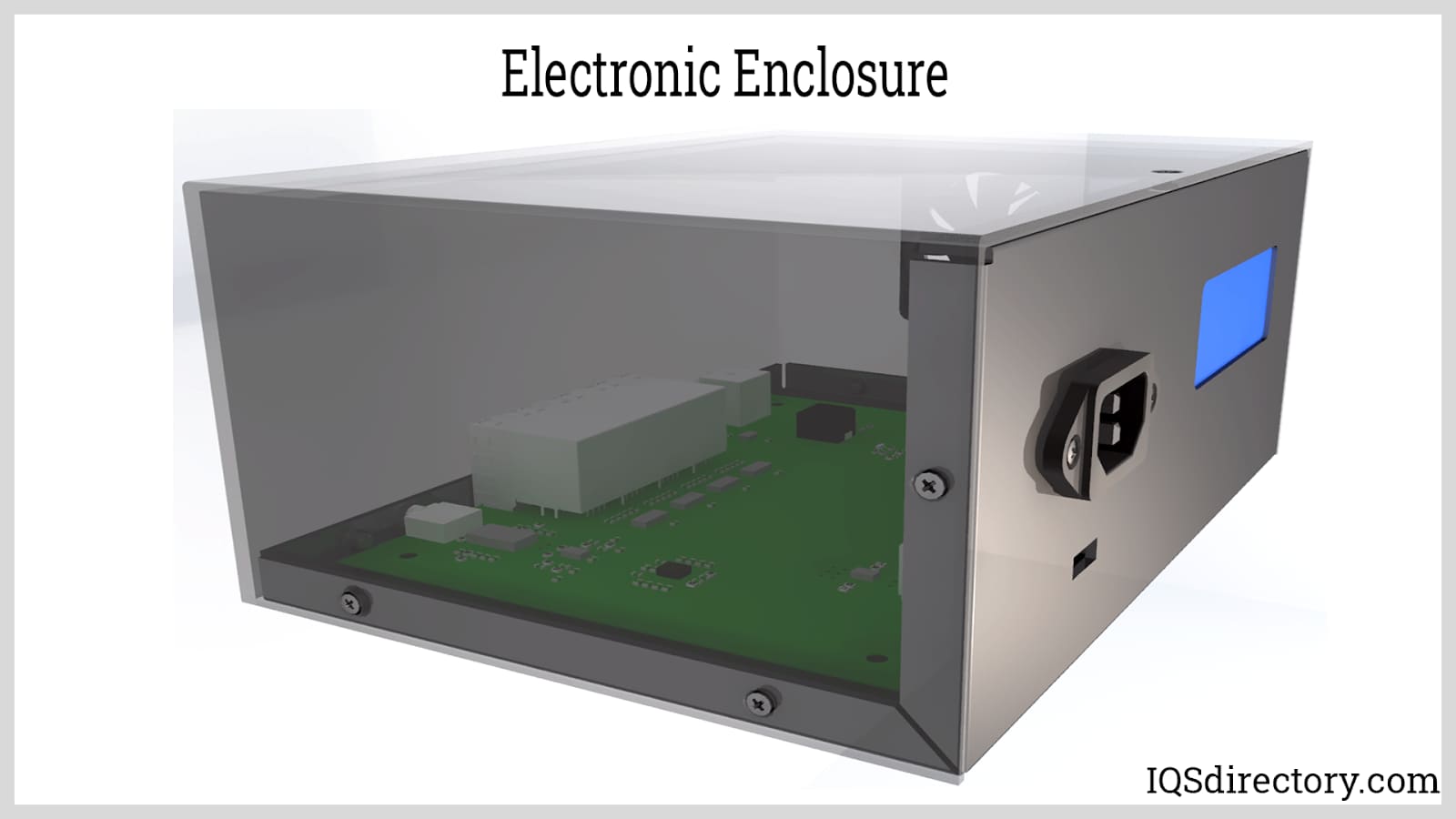
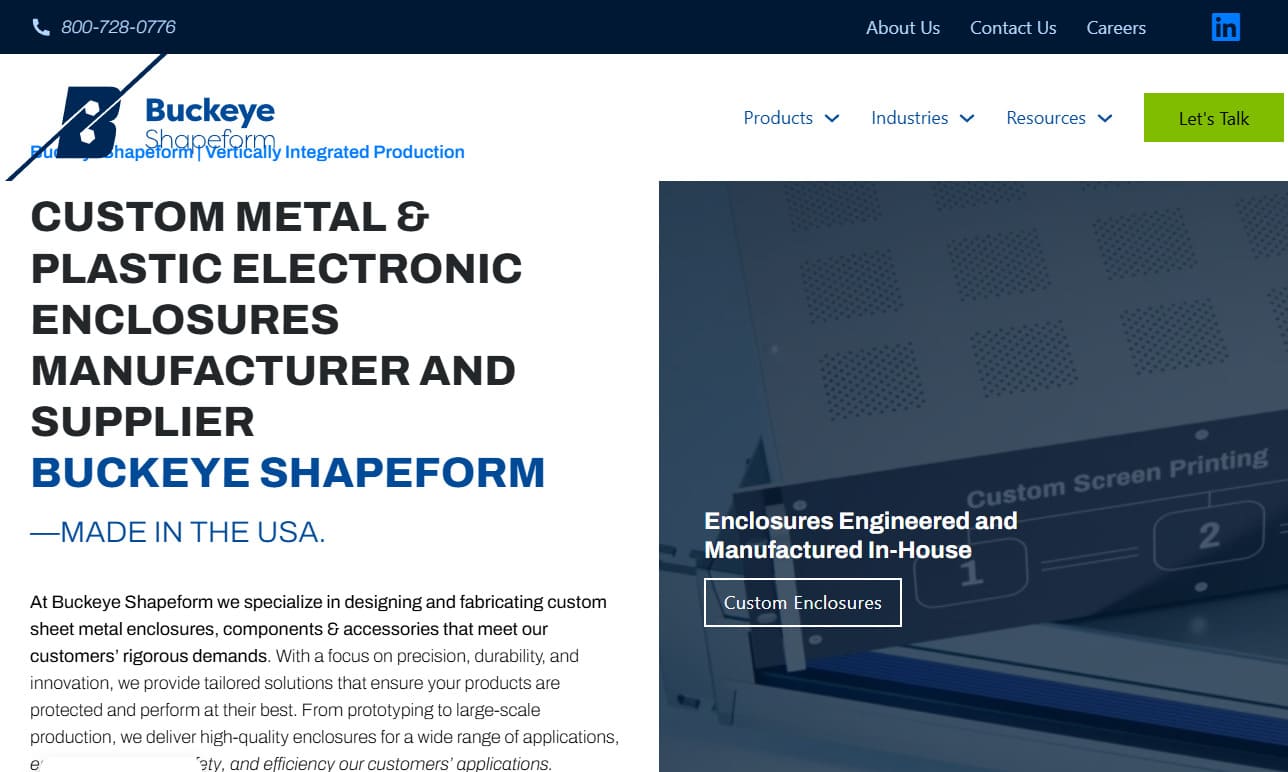
Electrical enclosures serve as protective housings for electrical and electronic equipment, ensuring safety, reliability, and longevity in a wide array of environments. Typically rectangular in shape, these enclosures are manufactured from materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, galvanized steel, polycarbonate, ABS, and other robust plastics. Their sizes range from compact enclosures—like those for LED flashlights or small circuit boards—to massive walk-in rooms housing industrial control systems and high-voltage components.
Are you searching for the right electrical enclosure for your application? Understanding the types, material choices, standards, and use cases is crucial for ensuring optimal equipment protection and regulatory compliance.
What Are Electrical Enclosures?
Electrical enclosures are purpose-built boxes, cabinets, or housings that encase electrical or electronic devices, components, and wiring. Their primary function is to safeguard sensitive contents from environmental hazards, unauthorized access, accidental contact, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). In addition to providing physical protection, enclosures help organize and manage power distribution, control equipment, and facilitate safe maintenance routines.
Electrical enclosures are integral to both residential and commercial settings, including:
- Industrial automation and factory controls
- Power distribution and substation control
- Telecommunications and network infrastructure
- Building management systems
- Renewable energy installations (solar and wind)
- Transportation systems
- Hazardous and outdoor environments
Common Styles and Form Factors of Electrical Enclosures
Electrical cabinets offer a secure, accessible housing for larger systems and are equipped with a door or removable panel to facilitate easy access to internal components. Other enclosure styles include:
- Portable enclosures – Compact and lightweight, designed for handheld or movable equipment.
- Desktop enclosures – Used for benchtop instruments, test equipment, and small control panels.
- Display enclosures – Feature transparent or clear panels for touch screens, meters, or visual indicators.
- Wall-mounted enclosures – Affixed to walls for space efficiency, often used in commercial or industrial settings.
- Cabinet enclosures – Large, free-standing units that house complex assemblies, such as motor control centers or power distribution units.
Although many enclosures have a boxy, rectangular profile, custom designs can be manufactured to accommodate unique equipment shapes, such as round enclosures for gauges and meters or contoured housings for specialized electronics.
Specialized Enclosure Features
Modern electrical enclosures may include:
- Clear or windowed panels for monitoring equipment status
- Integrated cooling or ventilation systems
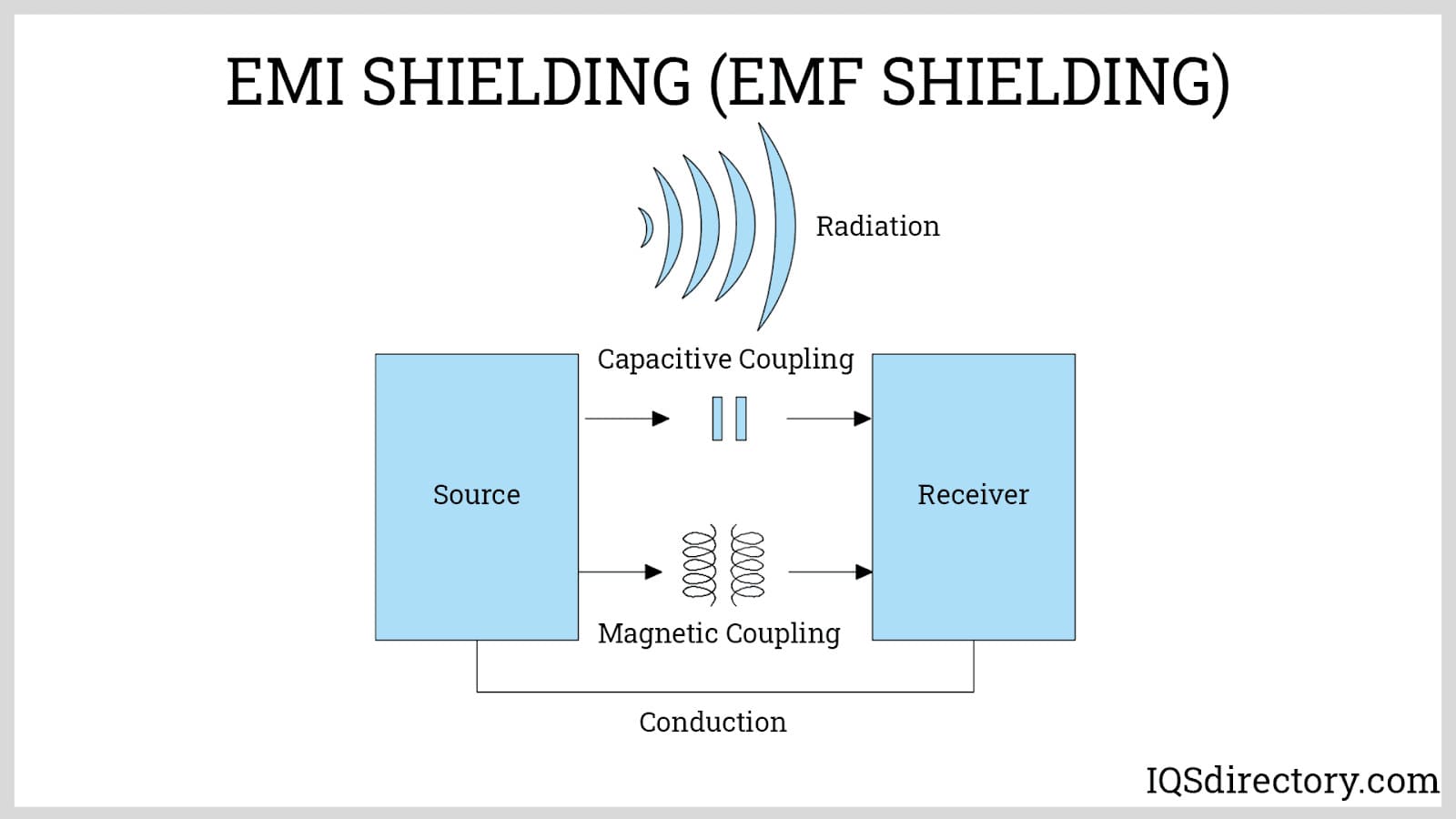
- EMI/RFI shielding for sensitive electronics
- Knockouts for cable and conduit entry
- Mounting provisions for DIN rails, terminal blocks, or PCBs
- Lockable doors and tamper-proof hardware for security
Materials Used in Electrical Enclosure Construction
The choice of enclosure material significantly impacts performance, durability, and suitability for specific environments. Common materials include:
- Aluminum: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and ideal for outdoor or marine applications. Aluminum enclosures are often extruded, meaning the metal is pushed through dies to create seamless, robust profiles.
- Stainless Steel: Offers superior corrosion resistance, strength, and hygiene, making it suitable for food processing, pharmaceuticals, and harsh industrial conditions. These enclosures are typically cold-rolled and welded for maximum integrity.
- Galvanized Steel: Economical and strong, with a zinc coating for basic rust protection. Used widely in indoor settings and low-humidity environments.
- Plastic (Polycarbonate, ABS, Fiberglass): Plastic electrical enclosures are lightweight, non-conductive, and resistant to many chemicals. These are often preferred for outdoor, wet, or corrosive settings and for housing sensitive electronics requiring insulation from EMI.
When do you need metal versus plastic enclosures? Metal provides superior strength, impact resistance, and EMI shielding, but may be heavier and more expensive. Plastics, on the other hand, offer excellent weather resistance, are easy to machine or customize, and are cost-effective for many light- to medium-duty applications.
Key Performance Features and Benefits
Why invest in high-quality electrical enclosures? The main advantages include:
- Environmental protection: Shielding against dust, water, oil, and corrosive agents.
- Electrical safety: Preventing accidental contact with live wires or energized parts, reducing the risk of electrical shock or fire.
- Equipment longevity: Extending the service life of internal components by isolating them from damaging external factors.
- Organizational efficiency: Streamlining wiring and component layout for easier troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting OSHA, NEC, and other safety standards for workplace safety and insurance requirements.
- Security: Limiting unauthorized access to sensitive controls or high-voltage areas.
- EMI/RFI shielding: Protecting sensitive electronics from electromagnetic and radio frequency interference.
Applications and Use Cases
Electrical enclosures are universal in their utility, found wherever electrical systems require protection. Typical applications include:
- Industrial automation: Housing PLCs, HMIs, motor starters, and control relays in manufacturing plants and process facilities.
- Power distribution: Safeguarding circuit breakers, switchgear, and transformers in commercial, residential, and utility settings.
- IT and telecom: Protecting servers, routers, and network equipment in data centers and telecommunication hubs.
- Renewable energy: Encasing solar inverters, battery storage systems, and wind turbine controls in outdoor installations.
- Hazardous locations: Explosion-proof enclosures for oil, gas, mining, and chemical processing industries.
- Transportation: Securing signaling, lighting, and communication systems in railways, airports, and roadways.
- Residential: Meter boxes, load centers, and smart home automation enclosures.
Looking for enclosures designed for specific environments? Contact us to discuss custom solutions and industry-specific requirements.
Industry Standards and Certification Ratings
Because electrical enclosures play a critical safety role, several standards organizations certify enclosures for specific conditions and uses. Understanding these ratings helps buyers select the right product for their application:
- NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association): NEMA ratings specify protection levels against ingress of solids, liquids, corrosive agents, and hazardous conditions. For example, NEMA Type 6P enclosures protect against dust, brief submersion, corrosion, and external ice formation. Other common NEMA types include Type 1 (indoor use), Type 3R (outdoor, rainproof), and Type 4X (corrosion-resistant, watertight).
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories): UL is a globally recognized certification body with its own set of standards for enclosure safety and performance. UL-listed enclosures have undergone rigorous testing for fire hazards, impact resistance, and environmental sealing. The UL mark is found on billions of electronics worldwide, signaling compliance with industry safety benchmarks.
- IP (Ingress Protection) Code: The International Protection Rating or IP Code classifies enclosures by their resistance to dust and water using a two-digit system (e.g., IP66 is dust-tight and protected against powerful water jets). The higher the IP rating, the more robust the protection against environmental hazards.
Wondering which enclosure ratings are required for your project? Review your local regulations and consult with a trusted manufacturer to ensure your enclosure meets all necessary codes and standards.
Comparing NEMA and IP Ratings
While both NEMA and IP ratings are designed to communicate the degree of protection an enclosure provides, they are not equivalent. NEMA ratings encompass a broader range of environmental and operational hazards, including corrosion resistance and construction features, while IP codes focus exclusively on dust and water ingress.
How to Choose the Right Electrical Enclosure
Choosing the best electrical enclosure depends on several factors. Ask yourself:
- What is the intended application (indoor, outdoor, industrial, residential)?
- What environmental hazards (water, dust, chemicals, temperature extremes) will the enclosure face?
- Will the enclosure need ventilation, cooling, or EMI shielding?
- How much space is required for equipment, wiring, and future expansion?
- Does the application require compliance with specific standards (NEMA, UL, IP)?
- Is there a need for security features (locks, tamper-proof hardware)?
- What is the available budget and total cost of ownership?
For guidance on enclosure sizing, layout, and configuration, explore our electrical enclosure resources or request a quote for custom fabrication.
Customization Options and Value-Added Services
Many manufacturers offer engineering support to customize enclosures according to unique project needs. Available options include:
- Custom cutouts and hole patterns for cable entry, switches, or displays
- Pre-installed gaskets, flanges, and mounting panels
- Color matching and powder coating for branding or visibility
- Laser engraving or silk-screen printing for labeling and identification
- Integration of cooling fans, heaters, or thermostats
- Assembly of internal wiring, connectors, and terminal blocks
Wondering how to customize your electrical enclosure for maximum performance and compliance? Contact our engineering team to discuss your specifications and receive expert recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Electrical Enclosures
- What is the difference between an electrical enclosure and an electrical cabinet?
An electrical enclosure is a general term for any protective housing for electrical components, while an electrical cabinet is typically a larger, free-standing type of enclosure with doors, often used for complex or high-voltage assemblies. - Can I use a plastic enclosure outdoors?
Yes, many plastic electrical enclosures—especially those made from UV-stabilized polycarbonate or fiberglass—are designed for outdoor use and withstand harsh weather conditions. Always check the enclosure’s IP or NEMA rating for suitability. - How do I determine the correct enclosure size?
Calculate the total volume of your equipment, allow for cable routing and airflow, and consider space for future expansion. Use manufacturer sizing guides or consult with an enclosure expert for assistance. - What are common accessories for electrical enclosures?
Accessories include mounting brackets, cable glands, ventilation fans, heaters, interior lighting, locking mechanisms, and nameplates for identification. - How do I ensure compliance with relevant standards?
Review local codes (such as NEC), select enclosures with the appropriate UL, NEMA, or IP ratings, and request documentation from your supplier to verify certification.
Top Considerations When Purchasing Electrical Enclosures
As you evaluate electrical enclosure solutions, keep the following decision factors in mind:
- Material selection: Match enclosure material to the environment, balancing durability, cost, and weight.
- Environmental resistance: Choose the right NEMA or IP rating for the hazards present in your application.
- Size and configuration: Ensure adequate space for all components and consider future scalability.
- Ease of installation and maintenance: Look for features that simplify field wiring, access, and serviceability.
- Customization: Opt for manufacturers offering flexible design, machining, and finishing services.
- Compliance and documentation: Confirm that enclosures meet all legal and regulatory requirements, and request certification records if needed.
- Supplier reputation: Partner with established enclosure manufacturers who provide technical support and stand behind their products.
Ready to compare enclosure options or request a quote for your next project? Visit our electrical cabinets page or submit your requirements online to get started.
Conclusion: Ensuring Safety and Reliability with the Right Electrical Enclosure
Electrical enclosures are fundamental to protecting people, equipment, and infrastructure across countless industries. With a wide selection of materials, sizes, designs, and certification ratings available, selecting the right enclosure is essential for optimal system performance and compliance with safety standards. By understanding enclosure types, materials, and ratings—and partnering with a knowledgeable supplier—you can ensure your electrical systems remain safe, reliable, and efficient for years to come.
Still have questions about electrical enclosures or need help with a specific application? Contact us for expert advice, or browse our electrical enclosure resources for additional information and buying guides.




 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services